SCC (Small-World Optimized)
In addition to the regular strongly connected component algorithm, we also provide a version that is optimized for small-world graphs. A small-world graph in this context means the graph has a hub community, where a vast majority of the vertices of the graph are weakly connected.
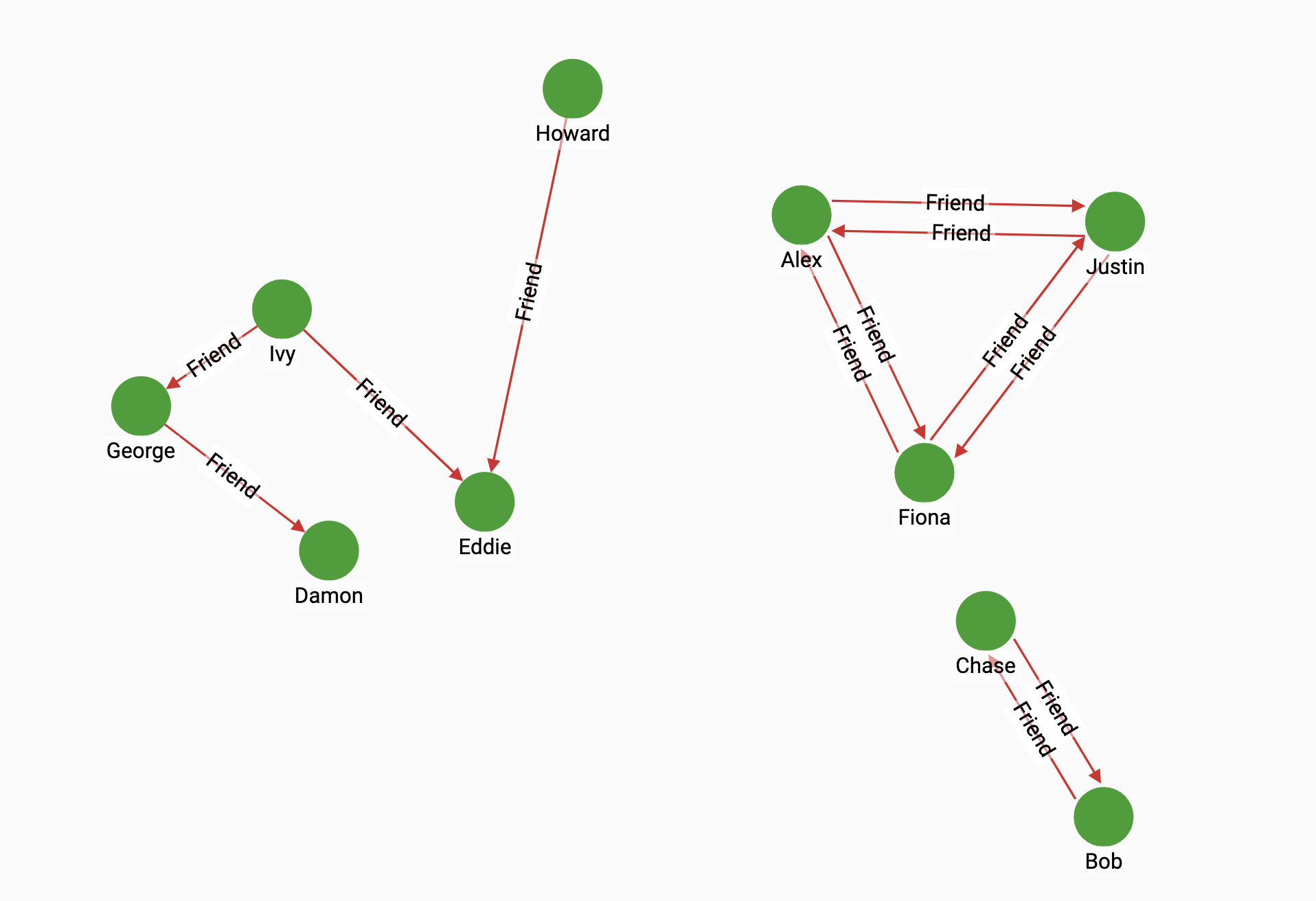
The algorithm starts by trimming the graph, which removes all vertices whose indegree or outdegree is 0. In the second phase, the algorithm selects an initial pivot vertex v with a high product of indegree and outdegree.
From the initial pivot vertex , the algorithm uses one iteration of the Forward-Backward method to identify all vertices reachable by v (descendants) and all vertices that can reach v (predecessors). The intersection of the descendants and the predecessors form a strongly connected component (SCC). The vertices that are not included in this SCC are passed off to the next step.
After identifying the first SCC, the algorithm uses the coloring method and Tarjan’s serial algorithm to identify the SCCs in the remaining vertices.
Notes
This version improves upon the performance of the original algorithm when dealing with small-world graphs by combining several different methods used to find connected components in a multi-step process proposed by Slota et al., BFS and Coloring-based Parallel Algorithms for Strongly Connected Components and Related Problems.
We use a default value of 100000 for the threshold used to choose initial pivot vertices to increase the chances that the initial pivot is contained within the largest SCC.
Specifications
CREATE QUERY tg_scc_small_world(STRING v_type, STRING e_type, STRING re_type, UINT threshold = 100000, BOOL to_show_cc_count=FALSE)
Parameters
| Name | Description | Data type |
|---|---|---|
|
The vertex type to count as part of a strongly connected component |
(empty string) |
|
The edge type to traverse |
(empty string) |
|
The reverse edge type to traverse. If the graph is
undirected, fill in the name of the undirected edge here as well as for
|
(empty string) |
|
The threshold used to choose initial pivot vertices. Only vertices whose product of indegree and outdegree exceed this threshold will be considered candidates for the pivot vertex. |
|
|
Whether to print the number of vertices in each strongly connected component. |
False |